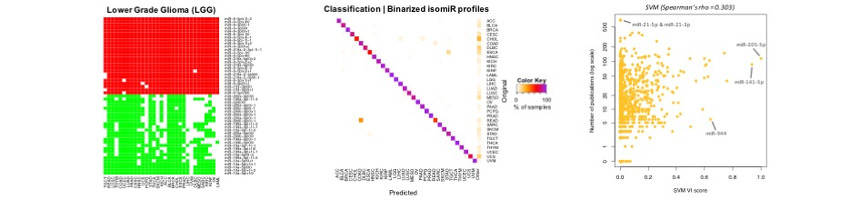
The concept of using of miRNAs as biomarkers is consistently becoming more and more popular but many studies do not address the problem of simultaneously discriminating among multiple cancer types. However, to identify biomarkers, they rely on the up- or downregulation of miRNAs in the cancer state for a given tissue. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) provides a unique opportunity to address this problem across more than 30 distinct cancer types with tumor samples from more than 10,000 individuals.
In our recent work1, we take advantage of well-established machine learning algorithms and build a computational model that relies only information on the presense or absence of miRNAs or their isoforms (isomiRs). Based on the TCGA 32 cancer types we train our model and achieve accurate predictions, not only for TCGA samples but also for samples analyzed with different platforms.
Our results support the notion for strong tissue-specific trajectories of cancer development (at least at the miRNA level) in addition to miRNAs commonly deregulated among cancers. However, the public literature remains heavily biased towards the latter features. Our work provides a complete framework and an Atlas on miRNA and isomiR expression across cancers that can serve as a tool for novel biomarker discovery and biomarker specificity evaluation.
References
- Telonis, AG, Magee, R, Loher, P, Chervoneva, I, Londin, E, Rigoutsos, I. Knowledge about the presence or absence of miRNA isoforms (isomiRs) can successfully discriminate amongst 32 TCGA cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45 (6):2973-2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx082. PubMed PMID:28206648 PubMed Central PMC5389567.