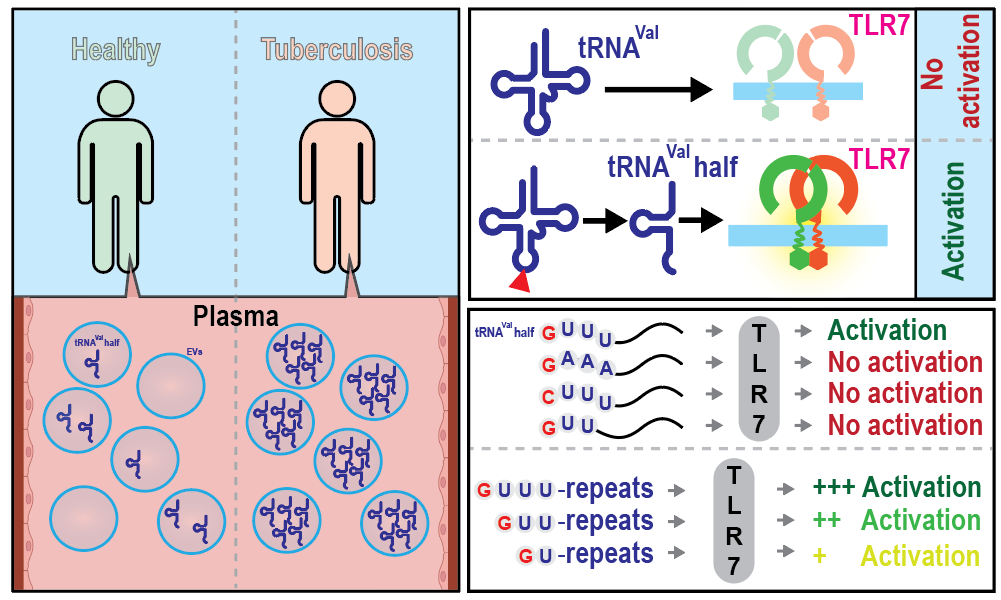
Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) is a vital component of the innate immune system, which also identifies single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs) as ligands. Dr.Yohei’s team have previously shown that TLR7 in extracellular vesicles (EVs) of human macrophages activate when extracellular (ex-) 5′-half molecules of tRNAHisGUG (the 5’tRNAHisGUG half) are delivered into it. Additionally, by comprehensively studying and analyzing immunostimulatory ex-5′-tRNA half molecules, the team also identified the 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half as another 5′-tRNA half molecule with strong TLR7 activation capabilities.
Macrophage EVs exposed to lipopolysaccharide and in the plasma of patients infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, have shown levels of the ex-5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half as highly up-regulated and half-mediated activation of TLR7, ultimately eradicating the bacteria infected macrophages. Mutation analysis of 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half identified the terminal GUUU sequence as a factor for the TLR7 activation. Past studies have confirmed that microRNAs, or any RNAs, with the terminal GUUU motif can jump-start TLR7 activation, thereby establishing the motif as a universal indicator of TLR7. These findings can provide diverse insights into TLR7-involved pathologies and their therapeutic strategies.
References
- Pawar, K, Kawamura, T, Kirino, Y. The tRNAVal half: A strong endogenous Toll-like receptor 7 ligand with a 5′-terminal universal sequence signature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121 (19):e2319569121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2319569121. PubMed PMID:38683985 .
