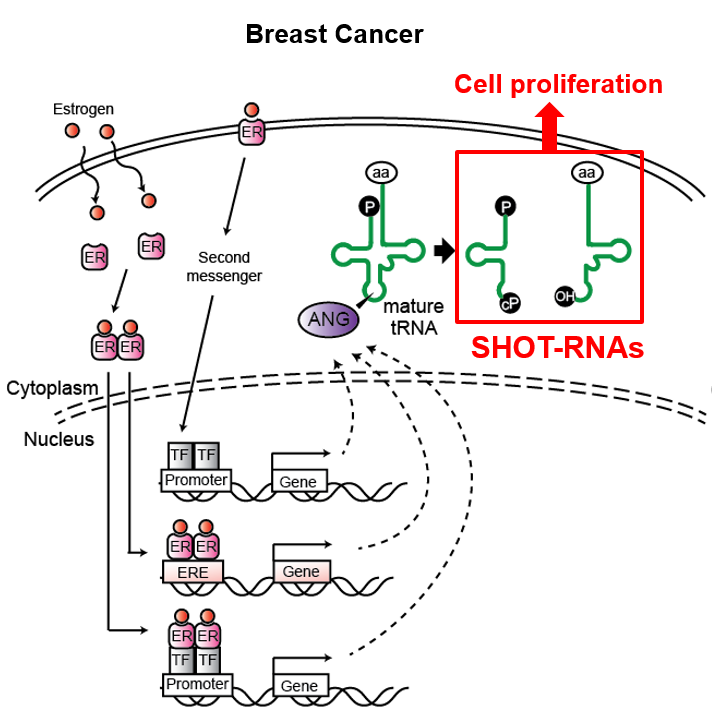
Sex hormones and their receptors play critical roles in the development and progression of the breast and prostate cancers. Here we report that a novel type of tRNA-derived small RNA, termed Sex HOrmone-dependent TRNA-derived RNAs (SHOT-RNAs), are specifically and abundantly expressed in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer and androgen receptor (AR)-positive prostate cancer. SHOT-RNAs are produced from aminoacylated mature tRNAs by angiogenin-mediated anticodon cleavage, which is promoted by sex hormones and their receptors. Resultant 5′- and 3′-SHOT-RNAs, corresponding to 5′- and 3′-tRNA halves, bear a cyclic phosphate (cP) and an amino acid at the 3′-end, respectively. By devising “cP-RNA-seq” method that is able to exclusively amplify and sequence cP-containing RNAs, we identified the complete repertoire of 5′-SHOT-RNAs. Furthermore, 5′-SHOT-RNA, but not 3′-SHOT-RNA, has significant functional involvement in cell proliferation. These results have unveiled a novel tRNA-engaged pathway in tumorigenesis of hormone-dependent cancers and implicate SHOT-RNAs as potential candidates for biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
 SHOT-RNAs promote cell growth in cancers
SHOT-RNAs promote cell growth in cancers
References
- Shozo Honda, Phillipe Loher, Megumi Shigematsu, Juan P. Palazzo, Ryusuke Suzuki, Issei Imoto, Isidore Rigoutsos, and Yohei Kirino. Sex hormone-dependent tRNA halves enhance cell proliferation in breast and prostate cancers. PNAS 2015 : 1510077112v1-201510077.
